Core Tips for Electronic Enthusiasts : The safety of patients and healthcare professionals is a top priority for medical electronics, but other factors such as the efficiency of electronic devices are also critical. The two factors of safety and efficiency pose conflicting demands on DC/DC power technology. The higher isolation gap and creepage distance required for medical grade enhanced isolation can result in the transformer's magnetic field not being optimally coupled, so traditional designs lose valuable efficiency. RECOM engineers have developed a new transformer concept that can circumvent this deficiency. The recently introduced "Re3-inforced" converter has a power rating of up to 6W, providing significantly improved isolation voltage levels and efficiency compared to conventional converters.
For industrial applications, industrial grade isolation is usually sufficient. In these applications, the primary and secondary windings of the transformer are interleaved with each other. Therefore, the internal magnetic field exhibits an ideal superposition state - this is a characteristic necessary to achieve high conversion efficiency. However, this design reduces safety because the two windings are only isolated by their respective enameled wire paint film. Under ideal conditions, the paint film can easily withstand test voltages of several thousand volts. However, damage caused during manufacturing or damage due to aging eventually leads to a short circuit between the primary winding and the secondary winding. Such failures can cause equipment failures in the field of industrial electronics – and in the medical electronics field, such failures pose a serious safety risk to patients and health care workers.

UL 60601 specifies limits for "enhanced" isolation
When designing equipment for medical applications, development engineers must be familiar with the specific provisions of IEC 60601. Various international standards have been consistent with EN60601 for the European market or UL60601 for the US market. These two national standards are similar in scope, but only those parts that are certified by Underwriters Laboratories can be labeled with the UL mark.
The basic electrical safety requirement for medical grade DC/DC converters is that the isolation barriers of these converters can pass the test of standard and fault voltages without failure. Since most medical applications are powered by mains, the generally accepted minimum isolation voltage is a sustained 264 VAC, which is equivalent to a 1600 VDC isolation test voltage lasting one second. In addition to being able to withstand the isolated test voltage, UL also specifies minimum creepage distance (trailing distance) and isolation gap (arc distance) for various isolation levels. Figure 2 is taken from the table published in the standard. It should be noted that the voltage specified in this table is the standard case input voltage, not the worst case fault isolation voltage.
The difference between isolation voltage and isolation level is often confusing. Medical grade DC/DC converters powered by 24VDC must be able to withstand isolation test voltages of at least 1600VDC/1 second, but 0.5mm isolation gap and 1mm creepage distance are sufficient to meet the standard requirements. The choice of isolation level is in the user.
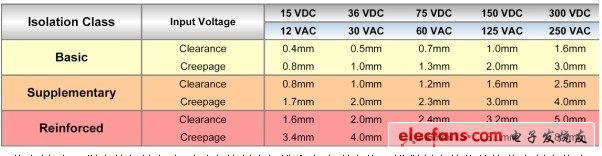
Figure 2: This table shows the isolation gap and creepage distance values ​​specified by the UL for the input voltage. The value of enhanced isolation is approximately three times higher than the basic isolation value.
Wuxi Juxingyao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.juxingyao.com