Kevin Kelly, the founding editor of Wired magazine, wrote an article about the five major misunderstandings of artificial intelligence in today's society and elaborated on the logic and theory behind it.
The following is the full text of the article:I heard the saying that in the future, computer-led artificial intelligence will be much smarter than us, and will even take away all our work and resources, and humanity will go extinct. Is that true?
Every time I talk about artificial intelligence, I always have to hear such questions. The questioners are very serious, and their concerns are partly due to the self-question and self-answer of various experts, including many of the most intelligent people in the world today, such as Stephen Hawking and Elon Musk. ), Max Tegmark, Sam Harris, and Bill Gates.
They all believe that this scene is likely to become a reality. In a recent seminar on artificial intelligence, a committee of nine big coffees agreed that this superhuman artificial intelligence is inevitable and not far away.
However, those who agree that superhuman artificial intelligence will eventually take over the world actually have five assumptions in mind. However, if you carefully analyze these five hypotheses, you will find that this is actually a "nonsense." These claims may become a reality in the future, but they have not yet been supported by evidence. The five basic assumptions about the rapid rise of superhuman intelligence are as follows:

1. Artificial intelligence has begun to transcend humanity and is evolving at an exponential rate.
2. We can develop general artificial intelligence like ourselves.
3. We can integrate human intelligence on silicon.
4, intelligence can be infinitely enhanced.
5. Once super intelligence is developed, it can solve most problems for us.
Contrary to these paradoxes, I think that the following five seemingly heretical ideas can be supported by more evidence.
1. Intelligence is not a single dimension, so the concept of “more intelligent than humans†has no meaning in and of itself.
2. Humans do not have universal thinking, and artificial intelligence does not have this ability.
3. Simulating human thinking on other media will be constrained by cost factors.
4. The dimension of intelligence is not unlimited.
5. Intelligence is just one of many factors that drive technological and social progress.
If the expectation that superhuman artificial intelligence takes over the world is based entirely on five key assumptions without evidence, then this idea is tantamount to religious belief. In other words, this can only be regarded as a kind of "myth". I have a good basis for the five tit-for-tat arguments put forward by these five hypotheses, which will be detailed in the following paragraphs. I will prove that the statement of superhuman artificial intelligence is just a "myth".
1
The most common misunderstanding about artificial intelligence comes from the general misunderstanding of natural intelligence. Many people think that intelligence is a single dimension, and this understanding is actually not correct. Most technicians tend to draw intelligent evolutionary maps like Nick Bostrom, who once described intelligence as a single dimension and linear development in the book Superintelligence. .
For example, one end is a small, intelligent little animal, and the other end is a highly intelligent genius—feeling intelligence is like a sound that can be quantified in decibels. Of course, if you agree with this view, you can naturally expand it, and think that the intensity of intelligence will further increase, and eventually exceed our own high intelligence state, become a super-intelligent, and even eventually burst.
This pattern is like a ladder, step by step progressively, and each level of intelligence is more progressive than the previous one. Lower animals are below us, and smarter artificial intelligence is bound to us. The specific time of occurrence is not important. What matters is the level – that is, the indicator of how good or bad the intelligence is.
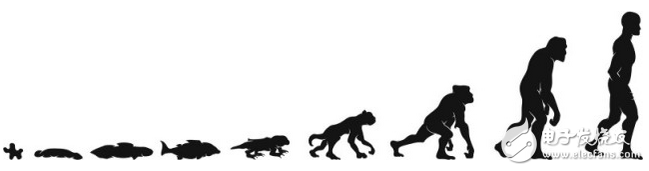
But the problem with this model is that it is just a misconception like an evolutionary ladder. Before the birth of Darwin's theory of evolution, people also believed that nature is a step-by-step development, with lower animals below humans. Even after the birth of Darwin's theory of evolution, this theory of stepped evolution is still very popular. This theory holds that fish evolved into reptiles, then evolved into mammals, evolved into primates, and eventually evolved into humans, each level progressing a little better than the previous level (and naturally more intelligent). Therefore, the smart ladder and the species ladder are parallel to each other. But in fact, neither of these models is in line with scientific concepts.
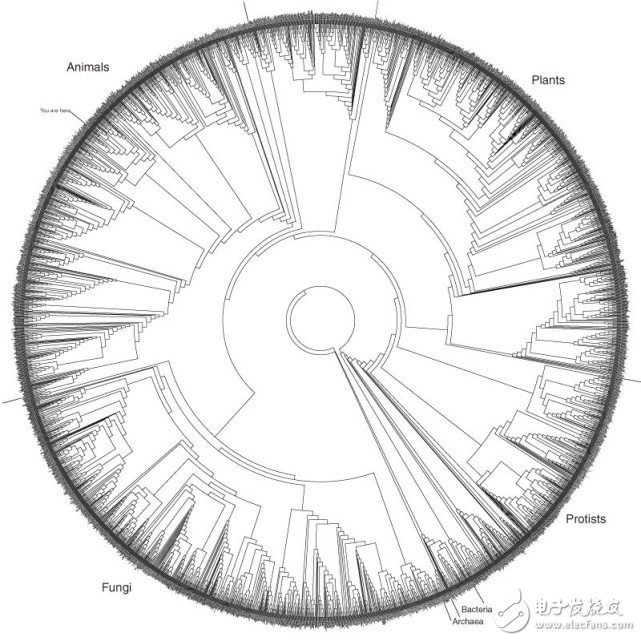
The above-mentioned disc diverging from the inside to the outside can more accurately describe the natural evolution of the species. This is the first drawing of DNA by David Hillis of the University of Texas. This in-depth pedigree classification model starts with the most central primitive life form and then diverges outward. As time goes by, it gradually forms the life form on the earth today, which is the outermost circle.
This picture highlights a fundamental fact of the evolutionary process: all species in today's world are equally evolving. Humans are located in the outermost circle with cockroaches, cockroaches, ferns, foxes, and bacteria. Each species has experienced a long-lasting development of 3 billion years and has successfully evolved to this day. This means that today's bacteria and cockroaches have the same level of evolution as humans, and there is no such thing as a ladder.
Similarly, intelligence also does not have a so-called ladder. Intelligence is not limited to a single dimension, but a complex of multiple cognitive types and patterns, each of which is a continuum. Let's talk about the simple task of measuring animal intelligence. If intelligence is a single dimension, then parrots, dolphins, horses, squirrels, octopuses, blue whales, cats, gorillas can be arranged in order. However, there is currently no scientific evidence to support such a sorting method. One of the possible reasons is that there is no difference in animal intelligence, but we also don't see this evidence.
There are many signs that can make a significant difference in thinking between animals. But do they all have relative "general intelligence"? This may be the case, but there is no indicator to measure this intelligence. Instead, we can evaluate different types of cognitive abilities through many different types of indicators.
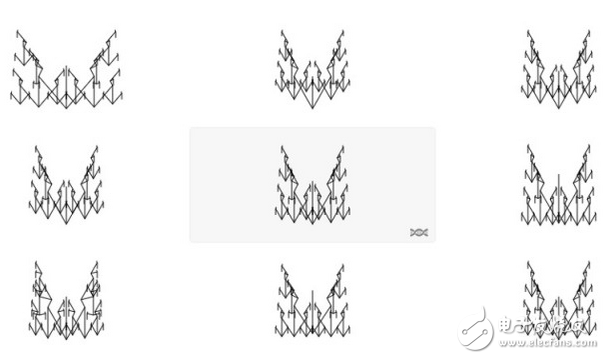
That is to say, there is no uniform indicator similar to decibel to measure the level of intelligence, so a more accurate intelligent model should be to draw its "possibility space". The above image is a table of possibilities generated using an algorithm written by Richard Dawkins. Intelligence is a collection of continuums. Various nodes (each node is a continuum) together form a multi-dimensional, diverse complex.
Some of the intelligence may be very complex, including many child nodes that symbolize various modes of thinking. Others may be simpler, but they are extremely extreme and are in the corner of the possibilities space. These complexes, which we call intelligence, are like a variety of symphonies, played by many different types of instruments. The difference between them is not only the loudness, but also the factors such as pitch, melody, tone, and beat. We can think of it as a set of ecosystems. In this sense, the nodes of different modes of thinking are interdependent and create symbiosis.
In the words of Marvin Minsky, human thinking is the society of mind. We operate on an ecosystem of thoughts that encompass a variety of cognitive abilities that form individual ecosystems like different species and can perform a variety of ways of thinking: deductive, inductive, symbolic reasoning Emotional intelligence, spatial logic, short-term memory, and long-term memory. The entire nervous system in our body is also a brain with its own cognitive patterns. When we think about it, we don't just use the brain, we use the whole body to think.
There are differences in cognitive abilities between different individuals and different species. Even after a few years, the squirrel can accurately remember the exact location of thousands of acorns. This skill has left several streets for humans. So in this cognitive ability, squirrels surpass humans. To form the squirrel's thinking, it is necessary to combine this "super power" with other modes of thinking that are dwarfed by human beings. The animal world has many other cognitive abilities that go far beyond humans, but they also need to be integrated into different systems.
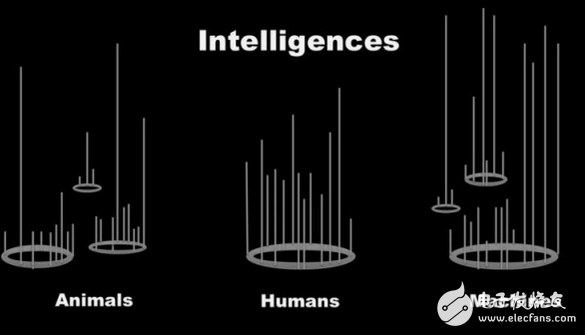
Artificial intelligence is also very similar. Artificial intelligence has surpassed humans in some dimensions. You can think of the calculator as a genius, and the memory of Google (microblogging) has already surpassed humans in some dimensions. We are developing artificial intelligence technologies that have superior capabilities in specific models. Some of these patterns are humans can do, but artificial intelligence performs better, such as probability statistics or mathematical calculations. There are also some abilities that we don't have at all - for example, remembering every word on 6 billion web pages, and that's exactly what search engines do.
In the future, we will develop new cognitive models that humans do not have, and some even have models that have never existed in the entire biological world. When we invented the man-made aircraft, it was inspired by the biological flight mode, mainly the wings that kept moving. However, the aircraft we invented installed a propeller on a larger fixed wing, which is an unprecedented flight mode in the biosphere and a special-shaped flight mode.
Similarly, we will develop new thinking patterns that have never been seen in nature in the future. In many cases, this is a specialized model designed for a specific task—perhaps a form of reasoning that works only in terms of statistics and probability.
In other cases, this new thinking can be a complex cognition that can help us deal with problems that cannot be solved independently using our own intelligence. The most difficult problems encountered in business and science may need to be solved in two steps: The first step: inventing a new mindset to match our thinking. The second step: combine the two and finally solve the problem.
Since we are solving problems that we couldn't solve before, we think that this kind of cognition is "smarter" than ourselves, but in fact, it is just "not the same" as us. This difference in thinking is the main advantage of artificial intelligence. I think that when it comes to artificial intelligence, the really desirable way is to think of it as a shaped intelligence (or artificial alien). The difference between it and us is its true value.
At the same time, we will incorporate these different cognitive models into a more comprehensive and complex “thinking societyâ€. Some of these complexes are more complex than us, and because they solve problems we can't solve, some people will define them as "superhuman." But we won't call Google a superhuman artificial intelligence, even if it has more memory than us, because we can do better than it in many things.
These artificial intelligence complexes can certainly surpass us in many dimensions, but no entity can fully surpass humans in all aspects. This is somewhat similar to the progress made in physical strength. The industrial revolution has been 200 years old. Although all machines as a whole can physically surpass human individuals (running speed, weight lifting ability, precise cutting), no single machine can completely surpass an ordinary person in all matters.
Even if the “thinking society†in artificial intelligence becomes more complex, it is currently difficult to measure this complexity scientifically. We don't have a set of viable complexity indicators to determine whether cucumbers are more complex than Boeing 747, or to determine if there is a difference in the complex ways between them.
It is very difficult to determine if thinking A is more complicated than thinking B. Similarly, it is very difficult to determine whether Thinking A is smarter than Thinking B. We will soon realize that the so-called "smart" is not a single dimension. We also realize that what we really care about is actually other modes of operation of intelligence—that is, all other cognitive nodes that we have not yet discovered.
2
The second misconception about artificial intelligence is that we believe we have universal intelligence. It is precisely because of this concept that has been repeatedly mentioned that artificial intelligence researchers often elaborate on one goal: to develop general artificial intelligence technology (AGI). However, if we look at intelligence in the "availability space" above, then there is no generality to say.
Human intelligence is not at the center, and other special intelligence is not developed around it. On the contrary, human intelligence is only a very specific form of intelligence. After millions of years of evolution, our species survived on Earth. If you understand the space in which all possible types of intelligence are located, you will find that human intelligence is just a “snapshotâ€, just as our world is on the edge of the vast Milky Way.
We can certainly imagine and even invent a multi-purpose thinking similar to the Swiss Army Knife. It can do a lot of things, but none of them can do the best. Artificial intelligence can't break through this limit: it's impossible to optimize for all dimensions, only trade-offs and compromises. It is impossible to develop a versatile general-purpose artificial intelligence that excels in every specific function.
A huge "all-round" thinking can't be as good as a dedicated artificial intelligence in everything. Because people think that human thinking is a general thinking, it is often believed that cognition does not have to be limited by the trade-offs of engineers. It is considered that it is possible to develop an intelligent technology that is the ultimate in all modes of thinking.
But I did not see any evidence to support this argument. We have not developed a sufficiently diverse mindset and thus cannot see the overall state of the possibilities space.
3
The reason why human beings think that they can achieve the ultimate in general thinking is in fact derived from the concept of general computing. This concept was previously called the Church-Turing hypothesis in 1950. This hypothesis holds that all calculations that achieve a particular threshold are equivalent. So all calculations have a common core: no matter whether the parts that make up a machine are fast or slow, even if they happen in the brain of an organism, they follow the same logic. This means you can simulate any computing process (thinking) on ​​any machine that can perform "general computing."
Singularists use this theory to support their expectations: they believe that we can make a "silicon brain" with human thinking, and even develop artificial ideas that can be thought like humans, and are far smarter than humans. We should be suspicious of this expectation because they misunderstood the Church-Turing hypothesis.
The starting point of this theory is: "If you have unlimited tape (storage) and time, all calculations are equivalent." The problem is that in the real world, no computer has unlimited storage and time. When you do real-time operations in the real world, this can even be a world of difference. That's right, if you ignore the time factor, all thinking is equivalent. Indeed, you can simulate human thinking in any matrix, provided you ignore the time dimension, or the real limitations of storage and memory.
However, if time is taken into account, it is necessary to restate this law: two sets of computing systems running on two very different platforms are unlikely to be equivalent in real time. It can also be said that the only way to make different mindsets equivalent is to have them run on an equivalent base. The type of calculation that your calculations can handle in real time depends largely on the physical factors on which it depends—as the complexity increases, the more obvious it becomes.
I will further extend this argument: the only way to achieve a thought process similar to humans is to do calculations on human flesh and blood. This means that the complex large-scale artificial intelligence constructed on the cold silicon wafers can generate complex large-scale thinking, but it is different from human thinking. If you can use artificial nerves like humans to develop bloody and artificial brains, their thinking may be more similar to us. The benefits of this flesh-and-blood brain are directly proportional to the degree to which the base on which it depends is similar to us. The cost of creating "wetware" (the human nervous system) is enormous, and the closer its organizational structure is to the human brain tissue, the more cost-effective it is to "manufacture" humans. After all, we can “manufacture†a person as long as we have nine months of pregnancy.
Also, as mentioned above, I use the whole body to think, not just rely on thinking. There is a lot of data to show how the human nervous system leads our “rational†decision-making process and even predicts and learns this process. The deeper we know about the entire human body system, the more likely it is to replicate it. Intelligence on different carriers (for example, from a flesh-and-blooded body to a cold silicon wafer) produces different ways of thinking.
I don't think this is a loophole, but instead think it's a feature that can be exploited. As I said in Article 2, having a different way of thinking with humans is precisely the advantage of artificial intelligence. For this reason, I think it is misleading to define it with the phrase "more intelligent than humans."
4
The core of superhuman artificial intelligence—especially the idea that this artificial intelligence will continue to self-improve—is that they believe that intelligence can have unlimited scale. I have not found evidence in this regard. Similarly, misconceptions that look at intelligence in a single dimension have contributed to this perception, but we should understand it. According to current scientific research, there is no physical dimension in the universe that is infinite.
The temperature is not infinite - there is a limit to both hot and cold. Space and time are not unlimited, and speed also has limits. The numbers may be infinite, but other physical properties have limits. So the question becomes: Where is the limit of intelligence? We often think that this limit is far beyond our ability to be "higher" than us, just like we are "above" ants.
Regardless of the recursion issue of a single dimension, do we have any evidence that human beings are not the limits of intelligence? Why can human intelligence not be the limit of intelligence? Or is it possible that human intelligence is only a short distance from the limit? Why do we think that intelligence can continue to improve indefinitely?
There is a better way to think about this problem, which is to think of our intelligence as one of the millions of possible intelligences. So while every cognitive and computational dimension has limitations, if there are hundreds of dimensions, there are countless types of thinking—no single type of thinking can reach an infinite height in any dimension. When we build and encounter these innumerable mindsets, we may naturally think that some of them are beyond us. In the recently published book The Inevitable, I elaborated on some types of thinking that can transcend us in some ways. Here are some of the excerpts:
- Similar to human thinking, but the answer is faster (this is the easiest to imagine artificial intelligence thinking)
——The thinking speed is very slow, mainly composed of huge storage and memory
——Collective super thinking consisting of millions of stupid individual thinking forces
- collective thinking consisting of many extremely intelligent thinking, but not aware that he is a collective
- There are many super-thinking ideas that are extremely clever in thinking, and they clearly realize that they have joined a consortium.
- it is trained and specifically designed to enhance your personal thinking, but not useful to others
- can imagine better thinking, but can't create it
- able to create better thinking, but not enough self-awareness to imagine this thinking
——Be able to successfully create better thinking in one go
- able to create better thinking, and this created thinking can also create a better thinking than it
-- Ability to access your own source code, so you can adjust your process on a regular basis.
- Super logical thinking without feelings
——Thoughts with general problem-solving skills, but no self-awareness
——Thoughts that have self-awareness but do not have the ability to solve common problems
- takes a long time to develop, and requires a set of thinking to act as a protector before maturity
——Distributed in the huge ultra-slow thinking, fast thinking seems to “can’t see†it
——Thinking with rapid self-replication ability
- able to self-replicate and still be able to integrate with your own clones
- Immortal thinking that can move from one platform to another
- Fast dynamic thinking that changes process and cognitive characteristics
- the smallest self-consciousness (whether size or energy) nano-thinking
- Good at specific scenarios and predictive thinking
- Never erase or forget things, or misunderstand any information
——The symbiotic thinking of half machine and half animal
- half machine, half human electronic thinking
——Using quantum computing thinking, the logic it uses cannot be understood by us.
Some people may now refer to these things as superhuman artificial intelligence, but the diversity and specificity of these ideas will lead us to use the new vocabulary "smart" and "smart" and generate new insights.
Second, people who believe in superhuman artificial intelligence assume that artificial intelligence can exhibit exponential growth (based on certain unconfirmed single parameters), most likely because they believe it has achieved exponential growth. However, there is currently no evidence that artificial intelligence is experiencing exponential growth – no matter which way it is measured.
The exponential growth I'm talking about means that the performance of artificial intelligence can double every time. What is the evidence? I can not find. If there is no evidence now, why is it that the future will happen? The only thing that can grow exponentially is the input data obtained by artificial intelligence, which is the resource used to generate intelligence. But the output performance does not grow as Moore's Law. Artificial intelligence can't double the performance every three years, and even double the performance every 10 years.
I have asked a lot of artificial intelligence experts, and there is no evidence that the performance of artificial intelligence has achieved exponential growth. They all said that there are currently no indicators to measure intelligence, and they have not done work in this area. But when I asked Ray Kurzweil, who was firmly optimistic about the rapid development of artificial intelligence, to ask evidence that artificial intelligence showed exponential growth, he said that artificial intelligence did not achieve explosive growth, but showed a hierarchy. Growth model.
He said: "Artificial intelligence needs to increase the complexity of calculations and algorithms every step of the way... so we can expect linear hierarchical growth, because every step needs to achieve exponential growth in complexity. And our ability in this area has indeed achieved exponential progress. There is not much difference between us and the cerebral cortex, so I think it is possible to achieve it in 2029."
Kuzwell seems to be saying that artificial intelligence itself does not exhibit exponential growth. Instead, efforts to develop artificial intelligence have shown this growth, and the actual output is only one step at a time. This is almost the opposite of the premise of the artificial intelligence explosion. This situation may change in the future, but artificial intelligence is clearly not showing an explosive situation.
Therefore, when we envisage the situation of “artificial intelligence outbreakâ€, we should not regard it as a cascade of prosperity, but should be envisioned as a new type of sporadic development. To illustrate with a more vivid metaphor, this is more like a Cambrian species explosion than a nuclear explosion. It is almost certain that the result of accelerated technology development is not the birth of “superhumans†but “supernormal humansâ€. In other words, it will be beyond our experience, but it may not be “higher†than us.
5
It is assumed that super artificial intelligence will take over the world. Another premise is that super artificial intelligence with almost unlimited capabilities can quickly solve many major unsolved problems. But this argument is not supported by much evidence.
Many people who agree that artificial intelligence will achieve explosive growth expect this technology to achieve rapid progress. I call this fabulous concept "thinkism." In their view: thinking ability or intelligence level is the only factor that hinders future progress. But this is completely the first paradox. (Many people who like to think also have such a belief: thinking is a magical super power, even omnipotent.)
Take the example of curing cancer and prolonging life. These problems can't be solved by thinking alone. It is impossible to find out the aging mode of cells and the decline process of chromosomes by "thinking". No matter how hard it is, it is impossible to read all the known scientific literature to understand the mode of operation of the human body. No super artificial intelligence can simply think about all the nuclear fission experiments in the present and the past, and then come up with nuclear fusion technology in one day.
In addition to thinking, in order to transition from an unknown to a known one, it must be supplemented with many elements. There are a lot of experiments that need to be done in the real world, and each experiment produces a lot of conflicting data, so further experiments are needed to establish the correct hypothesis. Simply thinking about potential data simply won't produce the right data.
Thinking (smart) is only part of science, or even a small part. For example, we don't have enough data to solve the problem of old age, and even the tip of the iceberg has not been uncovered. Specific to the operating mechanism of the organism, most experiments need time to slowly brew. Cell metabolism is very slow and cannot be accelerated. It may take years, months, or at least a few days to see the results.
If you want to know the situation of subatomic particles, it is impossible to get answers by thinking alone. It is necessary to build complex large physical facilities. Even today's smartest physicists are 1,000 times smarter than they are today, and without a collider, they can't acquire new knowledge.
Super artificial intelligence can undoubtedly accelerate the scientific process. We can make atomic or cellular computer simulations that speed up dramatically, but there are two factors that limit the actual effect of the simulator when it comes to making instant progress. First, simulators and models are faster than the objects they emulate because they cut down some factors. This is the natural property of the model or simulator. It's also worth noting that testing, reviewing, and validating these models still needs to be done in the normal time dimension to match their mock objects. In other words, the speed of verification of facts cannot really speed up.
Simplified results in the simulator are useful for filtering the most promising paths, so you can speed up your progress. However, it is impossible to transcend reality, and all real factors will have a certain impact. This is also a definition of "reality." As more details are added to the model and simulator, the limitations are encountered, so that the actual running speed of the simulated object is faster than the simulator that copies the real element 100%. This leads to another definition of "reality": after considering all the details and degrees of freedom, the fastest version is "reality."
If you can incorporate all the molecules in the cell and all the cells in the human body into the model, the simulator will not exceed the human body. No matter how hard you think, it still takes time to complete the experiment, no matter whether it is a real system or an analog system.
In order to reflect practicality, artificial intelligence must be applied to the real world, and the real world tends to limit their speed of innovation. If you don't experiment, you don't develop prototype products, you don't experience failures, and you don't interact with reality. Artificial intelligence can only think and can't get results. The so-called "smarter than humans" artificial intelligence can't get any discovery in a flash. Although the speed is found to be greatly accelerated by the advancement of artificial intelligence, to some extent, this kind of distinctive artificial intelligence will raise the question that humans will not ask, but even if it has much higher intelligence than ours, it does not mean that it can Make progress immediately. To solve problems, it is not enough to rely on intelligence.
Not only can the problem of curing cancer and prolonging life be solved by intelligence alone, but intelligence itself cannot be solved by intelligence alone. Singularists have a theory: once you develop artificial intelligence that is "smarter than humans," it will suddenly try to think and develop artificial intelligence that is "smarter than yourself," and then develop smarter. Artificial intelligence, until the ability to burst, becomes like God.
There is no evidence that thinking smart alone is enough to develop more advanced intelligence. This "thinking" is a belief. But there is a lot of evidence that in addition to a large amount of intelligence, it is necessary to experiment with data, trial and error, repeated questioning, and things other than intelligence to successfully invent new thinking.
In summary, my analysis of these claims may be wrong. We are still in the early stages of development, and we may find a common smart metric in the future, and we may also find that intelligence can become infinitely powerful in all dimensions. Because we know very little about intelligence (not to mention "consciousness"), the probability of artificial intelligence singularity is greater than zero. I think that all the evidence shows that the probability of its existence is very low, but still greater than zero.
So, although I don't agree with this possibility, my confirmation is related to the macro goals that OpenAI is adhering to, and the concerns of those smart people who are worried about superhuman artificial intelligence—we should develop friendly artificial intelligence and then engage Be clear about how to instill a self-replicating value similar to ours.
Although I believe that superhuman artificial intelligence may pose a threat to our survival in the distant future (and worth considering this issue), but because this probability is very low (according to current evidence), it should not affect our Science, policy and development direction.
Asteroids hitting the Earth will inevitably lead to disasters. The probability of this happening is greater than zero (so we should support the B612 Foundation), but it should not affect our climate change, space travel or even because of the possibility of asteroids hitting the Earth. Efforts in urban planning.
Similarly, current evidence suggests that the most likely outcome of artificial intelligence is not to become a “superhuman,†but that there will be hundreds of new “superhuman†thinking, most of which are different from humans, but none of them are universal. Smart, and no one can solve the major problems we face in an instant like God.
On the contrary, there will be countless kinds of intelligent technologies with limitations, working in a dimension we are not familiar with, surpassing our thinking in many aspects, and cooperating with us in time to solve existing problems and create new problems.
I understand the great appeal of superhuman artificial intelligence. I also hope that Superman will appear, but like Superman, this is just a fictional myth. Superman may exist somewhere in the universe, but the probability is low. However, mythology is also very useful. Once it is invented, it will not disappear. The idea of ​​Superman will never disappear. Since the idea of ​​superhuman artificial intelligence singularity has been born, it will definitely last forever.
But we should also admit that this is still only an idea similar to religious beliefs, and there is no scientific basis. If we carefully study the various evidences we have about artificial intelligence and natural intelligence, we will find that our vision of superhuman artificial intelligence is nothing more than a mythical misconception.
Many people in the isolated Micronesian Islands were able to get in touch with the outside world for the first time during World War II. The alien god sits in the body of the roaring bird, flies over their sky, puts food and objects on the island, and then goes back. Thus, there was a religion on the island that prayed that God could come back to put more supplies.
Even today, 55 years later, there are still many people waiting for God to drop supplies again.超人类人工智能å¯èƒ½ä¹Ÿä¼šæˆä¸ºä¸€ä¸ªä¸Žä¹‹ç±»ä¼¼çš„宗教。一个世纪之åŽï¼Œå½“人们回望这段历å²çš„时候,å¯èƒ½ä¼šæƒ³ï¼Œæ¤æ—¶çš„信仰者开始期待超人类人工智能éšæ—¶å‡ºçŽ°ï¼Œä¸ºä»–们带æ¥ä¸å¯æ€è®®çš„价值。年å¤ä¸€å¹´ï¼Œä»–们始终ç‰å¾…ç€è¶…人类人工智能的出现,相信它很快就能载ç€â€œç‰©èµ„â€é™ä¸´äººä¸–。
然而并没有出现真æ£çš„超人类人工智能。我们一直在ä¸æ–é‡æ–°å®šä¹‰è¿™é¡¹æŠ€æœ¯ï¼Œå¢žåŠ 它é¢ä¸´çš„困难,甚至å¯èƒ½åœ¨æœªæ¥é™åˆ¶å®ƒçš„å‘å±•ã€‚ä½†ä»Žå¼‚å½¢æ™ºèƒ½â€”â€”ç”±å¤šæ ·åŒ–çš„æ™ºèƒ½ã€è®¤çŸ¥ã€é€»è¾‘ã€å¦ä¹ å’Œæ„识构æˆçš„è¿žç»ç»Ÿä¸€ä½“——的广泛角度æ¥çœ‹ï¼Œäººå·¥æ™ºèƒ½å·²ç»åœ¨è¿™ä¸ªæ˜Ÿçƒä¸Šæ™®éå˜åœ¨ï¼Œè€Œä¸”会继ç»æ‰©æ•£ã€æ·±åŒ–ã€å˜å¼‚ã€å¼ºåŒ–。
之å‰æ²¡æœ‰ä»»ä½•ä¸€é¡¹å‘明能åƒå®ƒä¸€æ ·ç»™æˆ‘们的世界带æ¥å¦‚æ¤å¤§çš„改å˜ã€‚到本世纪末,人工智能å¯èƒ½ä¼šæ¸—é€å¹¶æ”¹å˜æˆ‘们生活ä¸çš„一切。ä¸è¿‡ï¼Œå…³äºŽè¶…人类人工智能的神è¯â€”—既有å¯èƒ½æ˜¯äººç±»çš„ç¦ç¥‰ï¼Œä¹Ÿæœ‰å¯èƒ½å¥´å½¹äººç±»ï¼ˆæˆ–者二者皆有)——ä»å°†å˜åœ¨ä¸‹åŽ»ã€‚毕竟,这ç§å¯èƒ½æ€§å¤ªè¿‡ç¥žç§˜ï¼Œè®©äººæ¬²ç½¢ä¸èƒ½ã€‚
Vibration Motor is in the original basis to add a vibrating head, made into a Dc Motor drive with a vibration motor. To produce the shaking force.
6V Dc Vibration Motor is introduced:
6V Dc Vibration Motor volume is generally greater than 15 mm, mainly used in massage chair, massage waist, handheld massager, etc.
Characteristics: small volume, strong vibration;
Features: small size, fast speed, stable performance, low price, can use battery drive,Can change the different materials of the pendulum head
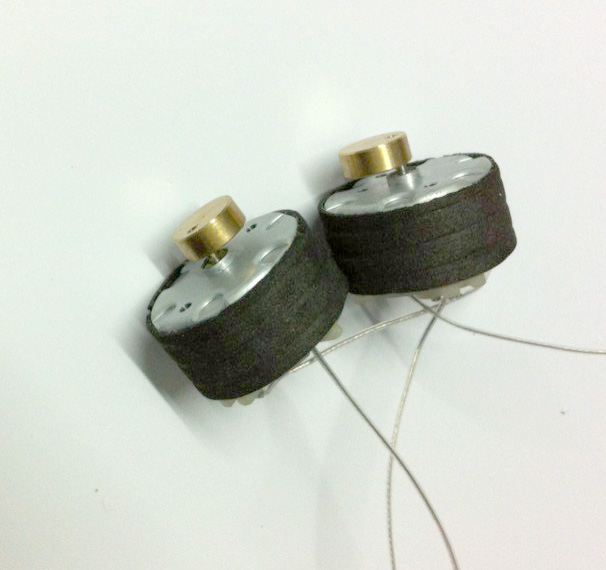
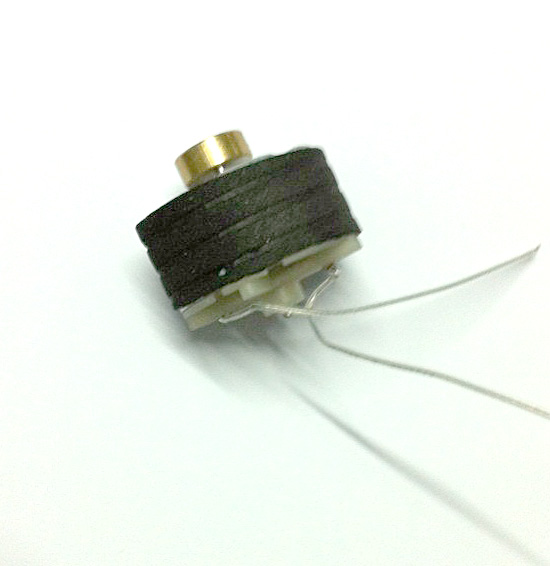

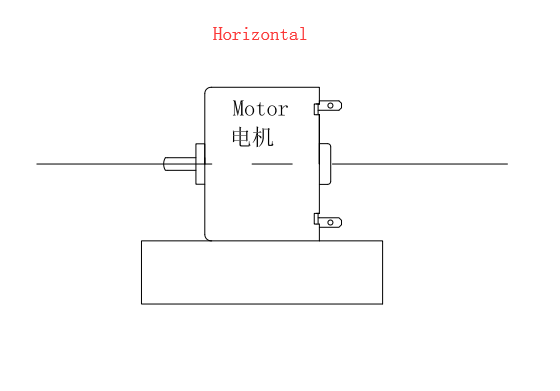
Method of use: the best stable in horizontal plane, installed on the dc 6V Dc Vibration Motor output shaft parts, cannot use a hammer to knock, knock prone to press into the dc 6V Dc Vibration Motor drive, may cause damage to internal components, and cannot be used in the case of blocked.
Operating temperature range:
6V Dc Vibration Motor should be used at a temperature of -10~60℃.
The figures stated in the catalog specifications are based on use at ordinary room temperature catalog specifications re based on use at ordinary room temperature (approximately20~25℃.
If a vibration motor is used outside the prescribed temperature range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.Depending on the temperature conditions ,it may be possible to deal with them by changing the grease of the motor's parts.Please feel free to consult with us about this.
Storage temperature range:
Dc Vibration Motor should be stored ta a temperature of -15~65℃.
In case of storage outside this range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.
Service life:
The longevity of Dc Vibration Motor is greatly affected by the load conditions , the mode of operation,the environment of use ,etc.Therefore,it is necessary to check the conditions under which the product will actually be used .The following conditions will have a negative effect on longevity.Please consult with us should any of them apply.
â—Use with a load that exceeds the rated torque
â—Frequent starting
â—Momentary reversals of turning direction
â—Impact loads
â—Long-term continuous operation
â—Forced turning using the output shaft
â—Use in which the permitted overhang load or the permitted thrust load is exceeded
â—A pulse drive ,e.g.,a short break,counter electromotive force,PWM control
â—Use of a voltage that is nonstandard as regards the rated voltage
â—Use outside the prescribed temperature or relative-humidity range,or in a special environment.
â—Please consult with us about these or any other conditions of use that may apply,so that we can be sure that you select the most appropriate model.
when it come to volume production,we're a major player as well .each month,we rurn out 600000 units,all of which are compliant with the rohs directive.Have any questions or special needed, please contact us, we have the engineer group and best sales department to service to you Looking forward to your inquiry. Welcome to our factory.

6V Dc Vibration Motor,Dc Vibration Motor,6V Dc Micro Vibration Motor,Small Size 6V Dc Vibration Motor
Shenzhen Shunchang Motor Co., LTD. , https://www.scgearmotor.com