Radio Frequency Identification Technology RFID (Radio Frequency IdentificaTIon) is a technology that uses radio frequency signals to automatically identify a target's ID to obtain object information and obtain related data. Different from traditional magnetic cards and IC cards, RFID technology solves the two major problems of passive and contact-free. At the same time, it can realize moving targets and multi-target recognition, and can be widely used in various occasions. Its outstanding advantages are strong environmental adaptability, ability to penetrate non-metallic materials, large data storage capacity, and strong anti-interference ability. According to different power supply methods, RFID can be divided into two categories: passive RFID and active RFID. When passive RFID works, the tag obtains energy through the electromagnetic field of the reader, and the tag itself does not require a battery. Active RFID is on the contrary, it needs to provide the power required for all devices to work, and the electronic tag needs its own battery. Compared with passive tags, active RFID temperature and humidity tags have the advantages of low transmission power requirements for readers and long effective reading distance. Therefore, they are used in cold chain logistics, medical systems, warehousing materials management, vaccine production logistics, and health and epidemic prevention systems. , Scientific research institutions and other aspects have a very wide range of applications. However, active RFID temperature and humidity Sensor tags have higher requirements for service life, reliability, and volume. Therefore, designing an active RFID temperature and humidity sensor tag with long life, high reliability, and small size is of great significance in national life. This article mainly solves the problem of low power consumption in active tag design.
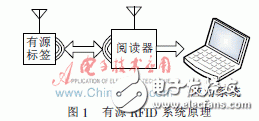
1 Active RFID system composition and working principleThe active RFID system consists of three parts: active tags, readers and application systems, as shown in Figure 1. Active tags have a unique identification code (ie ID), and some active tags have integrated sensors for measuring specific physical quantities. Within the effective working range of the reader, the electronic tag actively sends its ID and the measured physical quantity to the reader in the form of electromagnetic waves, and the reader stores the relevant information in its own storage device and in the reader The data can be transmitted to the application system through communication interfaces such as Ethernet port, RS-232, USB, etc. for further processing of the data.
2.1 Structure
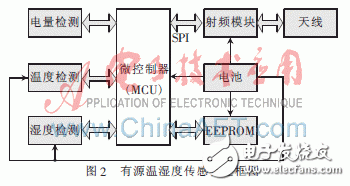
The structure diagram of the active temperature and humidity sensor tag designed in this paper is shown in Figure 2. The core of the active tag is a microcontroller (MCU), the radio frequency module receives/transmits radio frequency signals through the antenna; the EEPROM stores the identification code of the tag and the attributes of the item and other information; temperature detection and humidity detection are used to detect the tag respectively In order to simplify the design, the temperature and humidity of the environment can use a chip integrating temperature and humidity detection; the power detection module detects the battery voltage and indirectly detects the remaining power of the battery according to the relationship between the battery power and the voltage. ; The battery provides power for the normal operation of each module.
2.2 Overall circuit
2.2.1 Main control module
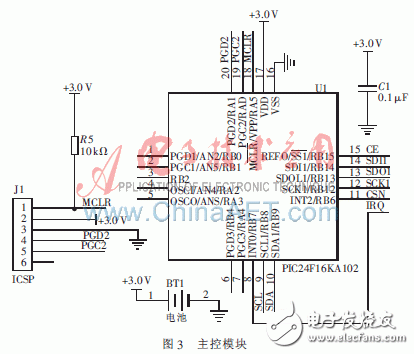
The main control module adopts a 16-bit ultra-low power single-chip microcomputer of Microchip's model PIC24F16KA102. The MCUs of this series adopt nanoWatt XLP (eXtreme Low Power) extremely low power consumption technology. The typical sleep current can be as low as 20 nA, the real-time clock current is as low as 490 nA, and the watchdog timer current is as low as 370 nA. MCU can run continuously for more than 20 years without battery replacement, becoming the MCU with the most outstanding low power consumption performance among the 8-bit and 16-bit MCUs in the industry. The microcontroller has SPI, I2C, UART, 9 analog input channels, 3 16-bit timers/counters, and 3 external interrupts, which can fully meet the needs of active tags. MCU and label carry on serial communication through SPI interface, as shown in Figure 3. J1 in Figure 3 is the ICSP interface used by the PIC 24F16KA102 microcontroller to download and debug programs.
2.2.2 RF transceiver module
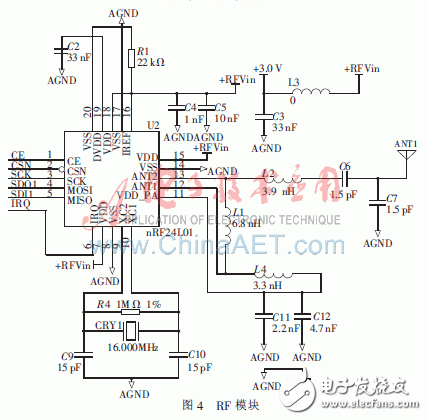
nRF24L01 is a single-chip wireless transceiver chip that works in the 2.4 GHz ~ 2.5 GHz universal ISM frequency band. nRF24L01 is mainly composed of modulator/demodulator, CRC encoder/decoder, GFSK filter, mid-band pass filter, power amplifier, low noise amplifier (LNA), first-in first-out buffer (FIFO). Carry on communication with MCU through SPI interface, its circuit diagram is shown as in Fig. 4. The nRF24LOT radio frequency transceiver chip has the following advantages:
(1) It has 125 optional working channels, which can be used for frequency hopping working mode, which can effectively reduce the interference of the surrounding environment.
(2) The QFN20 package area is only 4 mm & TImes; 4 mm, which occupies a smaller PCB area.
(3) Low power consumption. When working in transmit mode, when the transmit power is -6 dBm, the current consumption is 9.0 mA, while in receiving mode it is 12.3 mA, and the current consumption is lower in power-down mode and standby mode.
(4) With automatic response and automatic retransmission functions.
(5) Higher data transmission rate. It is 1 Mb/s when in ShockBurstTM mode and 2 Mb/s when in enhanced ShockBurstTM mode.
Incremental Encoder is commonly used, and Absolute Encoder is used if there are strict requirements on position and zero position. Servo system should be analyzed in detail, depending on the application situation. Commonly used incremental encoder for speed measurement, which can be used for infinite accumulation measurement; Absolute encoder is used for position measurement, and the position is unique (single or multiple turns). Finally, it depends on the application situation and the purpose and requirements to be realized.
Incremental Linear Encoders,Linear Optical Encoder,Linear Position Encoder,Encoder Bearing Tester
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yuhengcoder.com