Distance vector algorithm
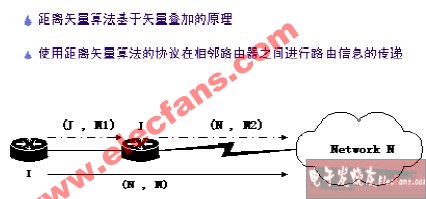
Distance vector algorithm is a routing algorithm commonly used in dynamic routing protocols. Its basic principle is to use vector superposition to obtain and calculate routing information.
The so-called distance vector is to consider a piece of routing information as a vector called by the target and distance (measured by Metric). Each router obtains routing information from its neighbors, and superimposes each routing information from itself to The distance vector of this neighbor forms its own routing information.
In the example shown in the figure above, Router I obtains the routing information (N, M2) from Router J to the target network N, where N indicates the target network and M2 indicates the metric value of the distance. And the distance vector from I to J (J, M1) is superimposed on this vector data to form the routing information (N, M) from I to the target network N, where M = M1 + M2.
This process takes place in each adjacent direction of the router. In this way, the router can obtain the path and distance to the target network in the network, and select the best path to form and maintain its own routing table.
LED Lighting Aluminum Alloy Die Casting
Led Lighting Aluminum Alloy Die Casting,Oem Aluminium Alloy Die,Led Zinc Die Casting,Aluminium Led Light Housing
Dongguan Metalwork Technology Co., LTD. , https://www.diecast-pro.com