Brushless DC motor is developed on the basis of brushed DC motor. It has the advantages of stepless speed regulation, wide speed regulation range, strong overload capability, good linearity, long life, small size, light weight and large output. A series of problems existed in brushed motors, widely used in industrial equipment, instrumentation, household appliances, robots, medical equipment and other fields. Since the brushless motor does not have a brush for automatic commutation, it is necessary to use an electronic commutator for commutation. The function of this electronic commutator is realized by the brushless DC motor driver.
Brushless DC motor is developed on the basis of brushed DC motor. It has the advantages of stepless speed regulation, wide speed regulation range, strong overload capability, good linearity, long life, small size, light weight and large output. A series of problems existed in brushed motors, widely used in industrial equipment, instrumentation, household appliances, robots, medical equipment and other fields. Since the brushless motor does not have a brush for automatic commutation, it is necessary to use an electronic commutator for commutation. The function of this electronic commutator is realized by the brushless DC motor driver.
At present, there are three main control methods for brushless DC motors: FOC (also known as vector frequency conversion, magnetic field vector orientation control), square wave control (also known as trapezoidal wave control, 120° control, 6-step commutation control). And sine wave control. So what are the advantages and disadvantages of each of these three control methods?

Square wave control
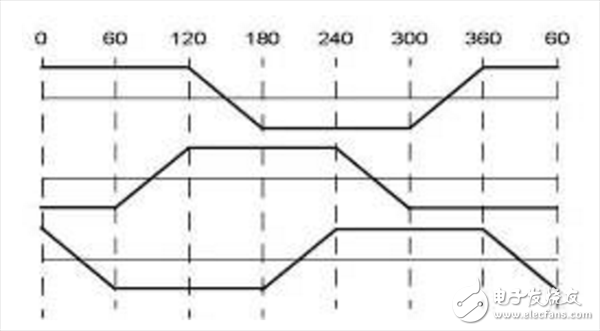
The square wave control uses the Hall sensor or the non-inductive estimation algorithm to obtain the position of the rotor of the motor, and then performs 6 commutations (every 60° commutation) according to the position of the rotor in the electrical cycle of 360°. Each commutating position motor outputs a force in a specific direction, so it can be said that the positional accuracy of the square wave control is electrical 60°. Since the phase current waveform of the motor is close to a square wave under the control of this mode, it is called square wave control.
The advantage of the square wave control method is that the control algorithm is simple, the hardware cost is low, and the controller with high performance can obtain higher motor speed; the disadvantage is that the torque fluctuation is large, there is a certain current noise, and the efficiency is not reached the maximum value. . Square wave control is suitable for occasions where the motor rotation performance is not high.
Sine wave control
The sine wave control method uses the SVPWM wave, and the output is a 3-phase sine wave voltage, and the corresponding current is also a sine wave current. In this way, there is no concept of square wave control commutation, or that an infinite number of commutations are performed in one electrical cycle. Obviously, compared with square wave control, sine wave control has less torque fluctuation and less current harmonics. The control feels more delicate. However, the performance requirements of the controller are slightly higher than the square wave control, and the motor efficiency cannot be achieved. Maximum value.
FOC control
The sine wave control realizes the control of the voltage vector, indirectly realizes the control of the current magnitude, but cannot control the direction of the current. The FOC control mode can be considered as an upgraded version of the sine wave control, which realizes the control of the current vector, that is, realizes the vector control of the stator magnetic field of the motor.
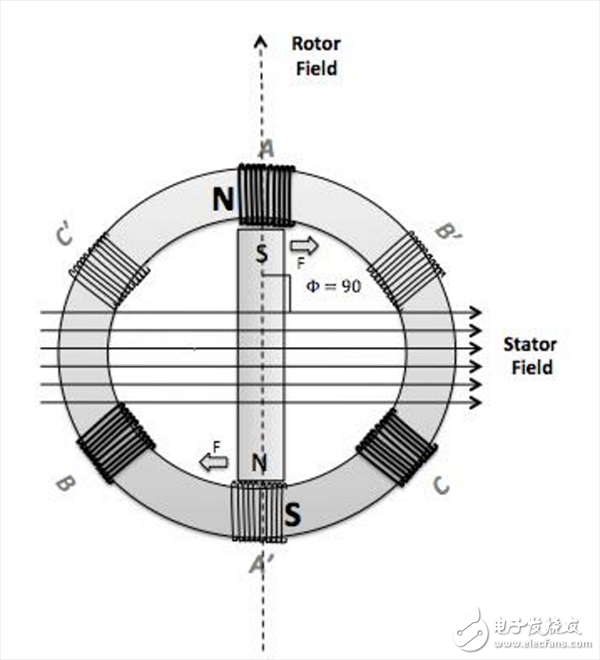
Since the direction of the stator magnetic field of the motor is controlled, the stator magnetic field of the motor and the rotor magnetic field can be kept at 90°, and the maximum torque output at a certain current can be realized. The advantages of FOC control mode are: small torque fluctuation, high efficiency, low noise and fast dynamic response; the disadvantages are: high hardware cost, high requirements on controller performance, and motor parameters need to be matched. Due to the obvious advantages of FOC, it has gradually replaced traditional control methods in many applications and is favored in the motion control industry.
Ceramic capacitor (ceramic capacitor);Ceramic condenser) is also known as porcelain capacitor or monolithic capacitors.As the name implies, ceramic dielectric vessel is a ceramic capacitor with dielectric material.According to different ceramic materials, this kind of capacitor can be divided into low-frequency porcelain dielectric vessel with capacity of 1-300 pF and high-frequency porcelain dielectric vessel with capacity of 300-22 000 pF.According to the structure type classification, can be divided into picture capacitor, tubular capacitor, rectangular capacitor, chip capacitor, piercing capacitor and so on.
Ceramic Capacitor,White Ceramic Capacitor,Smd Ceramic Capacitor,Multilayer Chip Ceramic Capacitor
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cndingweitech.com