On February 27th, the World Mobile Communications Conference MWC 2017 is about to kick off. This year's MWC will become a key node for 5G commercial acceleration. Operators such as Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, NTT docomo, Softbank, KT and Verizon will display 5G prototypes jointly with equipment manufacturers such as Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia at MWC 2017. Test the situation.
The fifth-generation mobile communication technology is considered to be the foundation of the Internet of Everything, and plays an important role in applications such as Internet+, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. A key advantage of 5G is that it will support mobile networks for more efficient operations and reduce data transmission costs. This is critical for mobile network operators to respond to new media and data-intensive use cases like AR/VR. With enhanced performance and a seamless user experience, enhanced mobile broadband use cases will support new application areas and needs in addition to supporting existing mobile broadband applications.
In addition to the enhanced mobile broadband use case, the proposed 5G specification will also include features that significantly extend the capabilities of current mobile technologies. This will support 5G's range of use cases including mission-critical services and massive IoT, requiring ultra-reliable and low-latency communications, as well as low cost and long battery life.

In this issue of intelligent internal reference, we recommend Qualcomm's customized IHS 5G industry report.
The following are the dry goods presented by the smart internal reference:
The 5G mobile network is the next major stage of the mobile telecommunications standard following the current deployment of 4G LTE. The IHS study focuses on the long-term economic impact of 5G, but it is also important to note that the 5G economy has begun to emerge. The 5G early commercial deployment, which is currently planned, has the potential to make a meaningful contribution to the economy by 2020.
The economic impact of new inputs, new R&D and new technology innovations suggests that 5G will have a profound and lasting impact on global growth. IHS Markit is convinced that 5G will be widely used in the global economy in the next two decades and will become one of the important contributors to the expansion of the global economy.

*IHS key research results
Status: next year's calibration ecological deployment has begun
3GPP is working hard to develop Release 15, which will be completed in 2018 and is expected to be the first specification for the new 5G wireless air interface (5G NR) and next-generation network architecture (5G NextGen).
5G development work will continue to 3GPP Release 16 and beyond, but Release 15 will provide global specifications for 5G commercials beginning in 2019. At the same time, the ongoing work of the 3GPP will be submitted to the ITU before the official release of the IMT-2020 specification, and the IMT-2020 specification will be completed in 2020. It is worth noting that while these specifications are being phased in, pre-standard 5G commercial deployments will start earlier.
From chipset and terminal vendors to network infrastructure vendors, the entire ecosystem has undergone significant pre-commercial work. Some operators have announced their timetable for 5G field testing. US operator Verizon said it will start in 2017, while South Korean operators SK Telecom and Korea Telecom are targeting 2018.
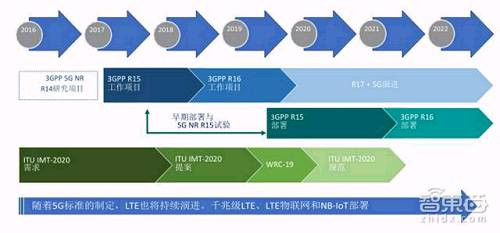
*5G standardization schedule (standard development and deployment)
Continuous investment and research and development to drive innovation and develop a new generation of technology is a necessary condition for realizing the full economic potential of the 5G economy. Accelerating the 5G economic process requires policy-makers to support long-term investment and R&D, and to achieve cooperation in the public and private sectors in the development of 5G standards to ensure that regulation and approval keep pace with innovation.
The challenge for policymakers in the 5G economy is that they must be prepared to face the spread of 5G technology in their daily lives and avoid creating systems that hinder continuous innovation.
As new business models emerge, the old ways of providing goods and services are drastically changed or abandoned altogether, and the 5G economy will bring greater complexity to policy development and regulation. Preparing for a 5G world will require modernization of policies and regulations in multiple areas, including public safety, cybersecurity, privacy, spectrum allocation, public infrastructure, health care, spectrum empowerment and approval, and education, training, and development.
Three types of use cases to achieve the Internet of Everything
5G has the potential to support high-reliability, ultra-low latency applications and build a widely available high-security network to create tremendous growth opportunities. Many use cases are still in their infancy (autonomous vehicles, commercial drones, telemedicine), and their growth will depend on market innovation, proper regulation, and 5G network deployment. Therefore, its rapid growth will take a long time, but given the broad significance of these use cases, it is expected to have a huge overall impact on society.
IHS Markit evaluated the technology diffusion cycles, popularity and potential long-term economic contributions of 21 foreseeable 5G use cases and classified them into three categories: enhanced mobile broadband, massive IoT and mission-critical services.
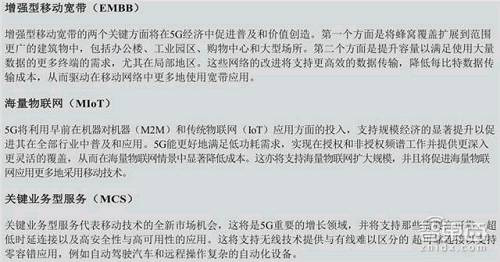
*5G three big use cases
Enhanced Mobile Broadband: Most likely to erupt in the near future
Enhanced mobile broadband use cases include:
1. Enhanced indoor wireless broadband coverage: Benefits include improved cellular coverage in buildings of all sizes, supporting wireless broadband coverage for a range of terminals and applications.
2. Enhanced Outdoor Wireless Broadband: Applications such as delivering high-definition infotainment content to cars, increasing outdoor activities and capacity in dense urban centers. Benefits include increased coverage and capacity in densely populated urban areas.
3. Fixed wireless broadband deployment: The main benefit of this use case is to support operators to provide more services without the need for high capital expenditures.
4. Corporate teamwork/collaboration: The benefits of this use case will be reflected by combining ultra-high definition transmission, virtual reality/augmented reality, video telepresence and tactile internet. These will enhance existing enterprise communications solutions and facilitate more dynamic interaction between team members and customers/end users.
5. Training/Education: Applied to corporate users (training) and traditional education (primary and secondary education and higher education), including remote and/or underdeveloped regions.
6, augmented reality and virtual reality (AR / VR): large-scale support for dynamic AR content requires 5G air interface. Low latency and multi-gigabit per second will support compute-intensive AR/VR user interaction. Specific use cases include outfield support and telemedicine.
7. Expand mobile computing: Combined with a wider wireless data pipeline and easy-to-access cloud computing, 5G smartphones will be able to handle productivity tasks that are always part of the laptop/desktop range.
8. Enhanced Digital Signage: With a combination of ultra-high definition and augmented reality technologies, 5G will support a wide range of applications from improving the retail experience to smart city applications. Benefits of this use case include real estate and home renovation, hotels and services, transportation and smart cities, all of which rely on digital signage.
These are mainly extensions of existing 4G values. With the commercialization of 5G networks, the market should have a faster spread. Enhanced mobile broadband use cases will have a major impact on global economic activity, but as most of its existing services are enhanced, its net economic impact will not be as transformative as massive IoT and mission-critical services.

Massive Internet of Things: 5G transformative
IHS Markit believes that 5G has the potential to address more of the machine-to-machine and IoT market and to reduce costs with economies of scale. Massive Internet of Things will be realized in the near and medium term, and will grow rapidly after the 5G massive IoT module is widely used. The use cases include:
1. Asset tracking: Monitor the distribution of assets (and personnel) on a large scale. In the current machine-to-machine market, the application will include personnel tracking and high-priced goods in transit. But (more) high connection costs limit the growth of the market.
2. Smart Agriculture: Its applications range from basic water storage facility monitoring to specialized sensors that monitor soil moisture and chemical composition. Benefits include optimizing irrigation and fertilization schedules, as well as optimizing growth and harvesting schedules. This helps improve farm operations efficiency and reduce manual labor needs. In addition, the “farm to market†reporting and accountability system can be improved to increase consumer transparency.
3. Smart Cities: Smart cities will provide opportunities for many different types of applications and potentially new business models, some of which include lighting, security, energy/utility, physical infrastructure environmental monitoring, and transportation/travel.
4. Energy/Utilities Monitoring: 5G can support proprietary networks, licensed and unlicensed spectrum, and multi-hop/mesh networks, which means it will combine the full benefits of competing technologies. This will make it easier for smart metering (all utility types) to be used by more types of utilities around the world.
5. Physical Infrastructure: Massive IoT features can be combined with networked sensors to significantly improve the monitoring of physical buildings (such as bridges and flyovers) and smaller buildings (such as elevators). In addition, geo-tagging allows visitors to use augmented reality to enhance the travel experience in large cities.
6, smart home: 5G can completely change the deployment and service methods of smart home terminals, it will solve some of the main problems of consumer complaints, such as terminal settings difficulties, equipment is not reliable, and the delay is too high.
7, remote monitoring: mainly industrial automation applications across a wide range of industries, the focus is on the use of universal sensing to support the device's progressive performance improvement and preventive maintenance. The potential of 5G is to provide a robust alternative to provide solutions for new and existing equipment.
8. Beacons and Connected Shopping: Enhancing the current retail technology's use of beacons and smartphones to improve the store's shopping experience. 5G will create potential not only for retailers, but also for products/brands in a more dynamic way. Interaction. In addition, beacons are beginning to gain popularity in industrial applications, and more robust wireless connectivity solutions will be the growth factor for this type of market.

Key business services: huge growth potential
Key business use cases include:
1. Self-driving cars: including broad categories of consumer and commercial applications. From the perspective of economic impact assessment, autonomous vehicles are one of the widely used use cases, especially for commercial vehicles and off-highway vehicles (farming, mining and construction).
2. UAVs: Widespread use of commercial drones will benefit many industries, including commercial transportation, agriculture, construction, manufacturing, and public safety. With the continuous improvement of drone technology, the demand for unmanned aerial vehicles by the company and the government will increase.
3. Industrial Automation: Most of the infrastructure in the factory floor will continue to be connected through wired connections, creating smarter factories, increasing workers and supporting plant asset mobility. It can create wireless solutions with high bandwidth and high security. Opportunity and can be achieved through 5G.
4, remote patient monitoring / telemedicine: 5G will reduce the dependence of patients, medical staff and monitoring equipment on different connection strategies. High-definition image quality enables more and more applications, including dermatology and wound care.
5. Smart Grid: If 5G can provide a cheaper and more comprehensive low-latency wireless network to the market, it will have the potential to open a huge use case for automated real-time grid switching. The economic impact can be significant because it will fundamentally create a more reliable grid.

Value chain: $3.5 trillion in output and 22 million jobs
IHS Markit estimates that by 2035, 5G will generate $12.3 trillion in potential sales worldwide and will span multiple industry sectors. This accounts for about 4.6% of the total global global output in 2035. During 20202035, global real GDP will grow at an average annual growth rate of 2.9%, with 5G contributing 0.2%. From 2020 to 2035, 5G contributed $3 trillion to annual GDP.
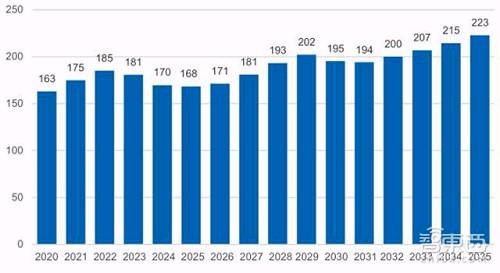
*5G Annual net contribution to global economic growth (in billions of US dollars)
By 2035, manufacturing will account for the largest share of all economic activity created by 5G – achieving about $3.4 trillion in output, or 28% of total 5G output. The information and communication industry will account for the second largest share of all economic activities created by 5G, exceeding $1.4 trillion. More notably, with the support of smart cities and smart agriculture deployments, 5G will create 6.5% of public service (government) output and 6.4% of agricultural output in 2035.
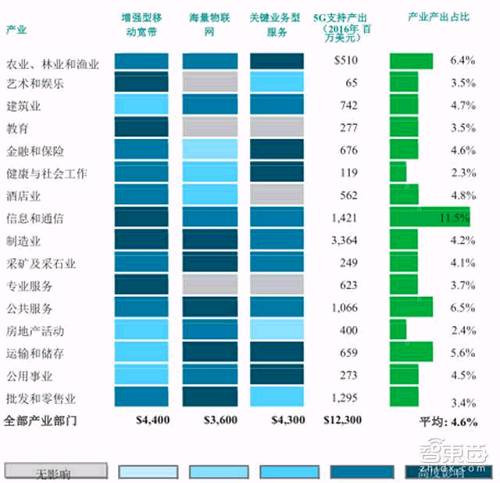
* 2016 5G globally driven economic activities (unit: billion US dollars)
The 5G value chain will cover a wide range of technology companies, including but not limited to network operators, core technology and component suppliers, OEM terminal manufacturers, infrastructure manufacturers, content and application developers. Seven countries will be at the forefront of 5G development: the United States, China, Japan, Germany, South Korea, the United Kingdom and France.
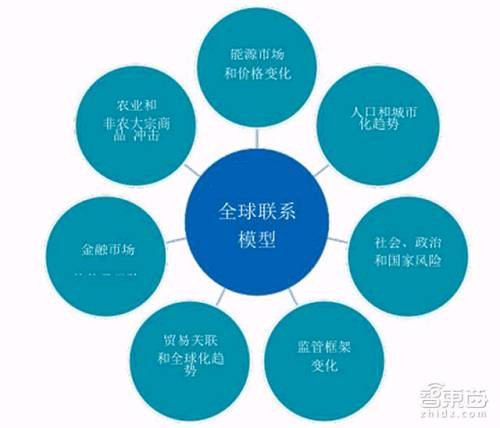
*5G industry global linkage model
IHS Markit expects that from 2020 to 2035, in the 5G value chain of the above countries, the average annual R&D and capital expenditures of related companies will exceed 200 billion US dollars. The United States and China are expected to lead 5G R&D and capital expenditures during the 16 years of this study. The two countries will invest $1.2 trillion and $1.1 trillion respectively.
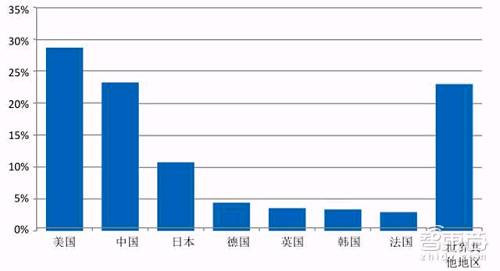
*20202035 5G value chain research and development and capital expenditure share (by country)
R&D and capital expenditures will drive the emergence of 5G use cases, creating sales in almost all industrial sectors, as well as throughout
The 5G value chain and its related supply network drive sales. IHS Markit expects that by 2035, the 5G value chain itself will generate $3.5 trillion in economic output while creating 22 million jobs.

*2035 global 5G value chain output and employment
Zhizhi believes that 5G will serve as a technology platform to connect cars and cities, hospitals and families, people and surrounding things in a more meaningful way. The industry is “specifically building†different aspects of the standard to address massive IoT-type applications as well as mission-critical use cases, including autonomous vehicles, industrial automation and telemedicine. These feature extensions will be deployed as part of a unified design, meaning that the same 5G infrastructure will be available to support a wide range of use cases.
Genki Ippai 1.0 uses high-tech temperature control, food grade pod and high-quality material device. We also upgrade to type-C interface for charging faster. We have developed various flavors for Genki Ippai Pod Systems. Up to 11 flavors provide consumers with more choices. What's more, you can use other brand`s vape pen with our vape pod.
We offer low price, high quality Disposable E-Cigarette Vape Pen,Electronic Cigarettes Empty Vape Pen, E-cigarette Cartridge,Disposable Vape,E-cigarette Accessories,Disposable Vape Pen,Disposable Pod device,Vape Pods to all over the world.
Pod Systems Vape And Smoke,Vape Pod System Device,Pod System Vape Kit,Pod System Mini Vape Pod
Shenzhen WeiKa Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.sze-cigarette.com