1 Introduction
Since the LED having high color performance, high efficiency, low carbon, energy-saving features, a large part of currently available LCD television began to use LED as a backlight. However, due to the variability of LED white light synthesis, many packagers' technicians are not well aware of how to choose a phosphor solution that matches the LCD under the known color gamut coverage requirements. At the same time, due to the different LCDs of various TV manufacturers, the technicians of the package manufacturers need to perform multiple and long-term package verification on the phosphor solution that meets the requirements of color gamut coverage and matches the LCD. This paper mainly explains and analyzes the conversion relationship between CF and white LED in LCD, the calculation method of color gamut coverage and how to choose the phosphor matching with CF in LCD under the requirement of known color gamut coverage. For reference by the packaging technician.
2. Description of LCD TV and color gamut coverage
2.1 LCD TV Introduction
LCD: Abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display, the full name of liquid crystal display, which includes TFT, UFB, TFD, STN and other types of liquid crystal display.
Liquid crystal: a substance between a solid and a liquid. It is an organic compound with a regular molecular arrangement. If it is heated, it will be in a transparent liquid state. If it is cooled, crystal particles will appear. Turbid solid state. Because of its characteristics, it is called liquid crystal. The liquid crystal molecular structure used for the liquid crystal display is similar to that of a fine match stick, and is called a Nematic liquid crystal. A liquid crystal display made of such a liquid crystal is also called an LCD.
LCD TV: A TV set that uses a liquid crystal display to make a display.
2.2 LCD construction and imaging principles
2.2.1 LCD construction
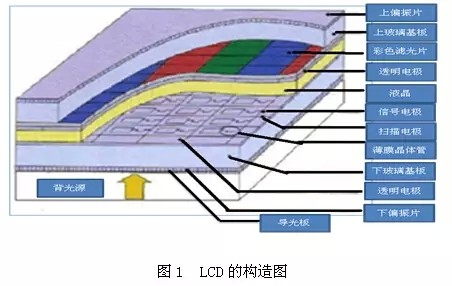
Taking a TFT type liquid crystal display as an example, the structure mainly includes a backlight, a light guide plate, an upper and lower polarizing plate, a liquid crystal, a color filter, a thin film transistor, etc. (the structure is shown in FIG. 1), and the main structural functions are as follows:
1. Back Light: The principle of LCD display is to block the light and light by the liquid crystal to control the light and dark. It is necessary to have a light source to see the image on the screen, so the backlight is responsible for providing the most basic for LCD display. Light source.
2. Light Guide Plate: distributes the light evenly across the entire screen;
3. Lower/Down Polarizer: The direction of the light sent by the backlight is inconsistent and radial. If such light passes through the twist of the liquid crystal molecules, we still can't see the image we want to see on the screen. At the time, the polarizing plate below assumes the work of normalizing the direction of the light to the liquid crystal layer.
4, thin film transistor (ThinFilmTransistor, TFT): control the twist angle of liquid crystal molecules
5. Liquid crystal (LiquidCrystal): This layer of liquid crystal molecules is twisted under the control of the TFT, and the light with the same direction is controlled to be bright, so that the brightness of the light to the rear pixel unit changes.
6. Color Filter: After the white filter is filtered, we can see that the light corresponding to the color of the filter is transmitted, so in the LCD screen, the function of the color filter is coloring.
2.2.2 LCD imaging principle
The principle of LCD imaging is to place the liquid crystal between two sheets of conductive glass. By controlling the driving of the electric field between the upper and lower polarizing plates and the upper and lower electrodes, the electric field effect of the liquid crystal molecules is twisted and nematic to control the transmission of the backlight or Masking, combined with other control and auxiliary function layers to achieve the function of restoring the picture.
2.2.3 LCD TV backlight introduction
Since the liquid crystal must be illuminated by an additional light source, the backlight used in LCD TVs is CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp)
CCFL vs. LED:
CCFL--made of hard glass and trichromatic phosphors. The tube has proper amount of mercury and inert gas. The inner wall of the tube is coated with phosphor and there is one electrode at each end. The disadvantage is that the color is limited. .
LED--a semiconductor solid-state light-emitting device that uses a solid semiconductor chip as a light-emitting material to recombine excess energy in a semiconductor by carrier to cause photon emission, directly emitting red, yellow, blue, green, cyan, and orange. , purple, white light. Because LED LEDs have good color performance, they have completely replaced the light source of traditional cold cathode fluorescent tubes.
2.3 gamut coverage
2.3.1 Meaning of gamut coverage
Color Gamut: refers to the range of the number of colors that a display system can express.
In order to be able to visually represent the concept of color gamut, the CIE International Lighting Association has developed a method for describing the color gamut: the CIE-xy chromaticity diagram. In this coordinate system, the gamut range that each display system can represent is represented by a triangular area composed of RGB three-point lines. The larger the area of ​​the triangle, the larger the gamut range of such a display device.
Color gamut coverage: The horseshoe-shaped chromaticity triangle marked with color on the CIE-xy chromaticity diagram is the color area that the human eye can see. If a system can fully reproduce the color in this horseshoe-shaped area, it can be said to be color. The domain coverage is 100%. The triangular regions composed of the three primary color coordinates of R, G, and B when the colors are reproduced by R, G, and B are the color reproduction regions determined by the three primary colors, and the ratio of this region to the horseshoe region is the color gamut coverage. Therefore, the gamut coverage ratio is the ratio of the area of ​​the triangular area composed of three basic color coordinates of R, G, and B to the area of ​​the triangular area composed of the three primary color coordinates of the standard R, G, and B.
Usb C Cable is also known as Usb Cable Type C interface,is an interface specification consisting of a Type-C plug and a type-C socket.Its highlights are thinner design,faster transmission speed (up to 10Gbps),stronger power transmission (up to 100W).In addition, USB-C interface also supports double-sided insertion,front and back can be inserted at will, compared with USB2.0/USB3.0 more advanced.Usb-c has been given better media properties,faster transfer speeds,and better compatibility with charging.The new generation USB-C has faster transmission speed than USB,stronger power transmission, smaller interface size,and supports bidirectional transmission with stronger compatibility.
Thinner bodies require thinner ports,which is one of the reasons USB-C is here to stay.The USB-C port is 0.83 cm long and 0.26 cm wide.The old USB port measuring 1.4cm long and 0.65cm wide looks outdated.This also means that the end of USB Cable will be one-third the size of the plug of A standard USB-A cable.The USB-C port is the same on the front and back.This means that no matter how you insert the port,it will be correct.Users do not have to worry about the pros and cons of traditional USB ports.

Usb C Cable,Custom Usb C Cable,Flexible Usb C Cable,Braided Coiled Usb C Cable
Henan Yijiao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.yjusbcable.com