introduction
In recent years, due to its small size, low power consumption, long service life, environmental protection, wide color gamut, and high brightness, Light Emitting Diode (LED) has gradually become the preferred light source for LCD backlights. Over 60%). However, the use of LEDs as liquid crystal display sources also has inherent defects: about 70% of the input power of LEDs is converted into thermal energy, which causes the temperature of LEDs and backlights to rise sharply, especially when multiple high-power LEDs are used simultaneously. When the fever is more serious [1].
TRIZ theory overview TRIZ theory is based on the analysis of a large number of patents by the former Soviet inventor Genrich Archie Schuler and his collaborators.
The legendary model followed by the development of technology and the innovative principles and rules for solving various engineering contradictions, the famous innovation theory (TRIZ) proposed in 1946 [2]. TRIZ theory believes that the core of the invention problem is to resolve contradictions. The constant discovery and resolution of contradictions in design is the driving force to promote the evolution of products to idealization; idealized design is the evolution direction of the system. At the beginning of TRIZ to solve the problem, the first is to determine the final The ideal solution, in the process of innovation, with the direction of increasing the level of idealization as the design goal. TRIZ theory successfully reveals the inherent laws and principles of creating inventions, focuses on revealing and emphasizing the contradictions existing in the system, rather than escaping contradictions; its ultimate goal is to completely resolve the contradictions and obtain the final understanding, rather than adopting compromises or compromises. The practice of researching the entire design and development process based on the evolutionary laws of technology is no longer a random behavior. Therefore, the innovation of TRIZ theory has high efficiency and stability.
3 LED backlight heat analysis
In the backlight of a liquid crystal display using an LED light source, the light input mode of the LED generally adopts a side-in type, and the light emitted by the LED is uniformly propagated to all directions of the backlight by the light guide plate. The biggest advantage of this is that it can achieve a thin design, but it also brings a problem, that is, heat dissipation.
3.1 LED heating mechanism
There are two reasons for LED heating: (1) Electrons will encounter resistance in the entire distance from the semiconductor region to the semiconductor region, thereby generating Joule heat; (2) Since the refractive index of the LED chip material is larger than that of the surrounding medium Much of the result, most of the light generated inside the chip can not smoothly escape the interface, and the full emission is generated at the interface between the chip and the medium, returning to the inside of the chip and being absorbed by the chip material or substrate through multiple internal reflections, and being latticed. The form of the vibration becomes heat, causing the junction temperature to rise. Comprehensive current injection efficiency, radiation luminescence quantum efficiency, chip external light escape efficiency, etc., finally only about 30% to 40% of the input electrical energy is converted into light energy, and the remaining 60% to 70% of the energy mainly occurs at the point where non-radiative recombination occurs. The form of the array vibration is converted into heat.
3.2 The effect of rising junction temperature on LED
LEDs generate a lot of heat, and if they are not released in time, the temperature of the chip will rise sharply. The increase in the temperature of the chip enhances the non-radiative recombination, further weakens the luminous efficiency, produces significant light decay, and significantly reduces the lifetime of the light source. In addition, LEDs are mostly encapsulated in transparent epoxy. If the junction temperature exceeds the solid phase transition temperature (usually 125 ° C), the packaging material will change to rubber and the thermal expansion coefficient will rise sharply, resulting in LED open circuit and failure [4].
The relationship between the LED illumination wavelength and temperature is:
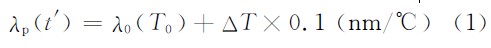
It can be seen from the formula (1) that the wavelength drifts to the long wave by 1 nm for every 10 ° C increase in junction temperature.
Technological advances in various aspects such as packaging; Secondly, the use of a good heat dissipation structure to dissipate the heat generated by the LEDs in a timely manner is a key measure at the current stage in the low luminous efficiency of LED products.
At present, the backlight is generally used to add a heat sink [5] (generally aluminum foil or aluminum plate) on the side where the LED light bar is placed, and uses heat conduction and convection to dissipate heat, which belongs to passive heat dissipation, and has the following disadvantages: heat dissipation The function is limited, generally only reduces the temperature by about 20%, and when the number of LED lamps is large, the area of ​​the heat sink will be extremely large, which will significantly increase the weight of the backlight, and the backlight is light and thin.