The LIN Association released the first version of the LIN protocol in 1999. It has been more than ten years. During these decades, the LIN bus has been continuously developed and has been applied in many occasions where body control is the mainstay. There are 7 versions of the LIN bus so far. Among them, the LIN2.1 protocol was released in November 2006 and is a newer version. It is almost the same as the latest LIN2.2 protocol, but it is significantly improved than its predecessor LIN2.0 protocol. It is mainly reflected in the addition of competition processing of event-triggered frames, improvement of node configuration functions, and diagnostic classification. aspect. These improvements allow users to organize the LIN network more conveniently and quickly, and can reset the LIN network according to their own needs, which not only ensures the stability of the product, but also meets the user's personalized needs. It is very important in the development process of the LIN bus itself A meaningful step.
1 New features of LIN2.1 protocol
1.1 Event triggered frame contention processing
If more than one slave node responds to the frame header in the same frame slot, it will cause contention, and the contention processing is all done by the master node. LIN2.0's event-triggered frame contention processing mechanism is shown in Figure 1. There are unconditional frame A, event triggered frame and unconditional frame B in the schedule of a certain master node. When the competition occurs, the master node will continue to follow the previous schedule, after receiving all unconditional frames related to the event trigger frame, and then send the event trigger frame header. LIN2.1 has made improvements to this. It introduces a competition processing schedule. The LIN2.1 event trigger frame competition processing mechanism is shown in Figure 2. Each event trigger frame has a competition processing schedule corresponding to it. After the master node processes the competition in the competition processing schedule, it returns to execute the ordinary schedule. Obviously, the contention processing mechanism of LIN2.1 takes less time.
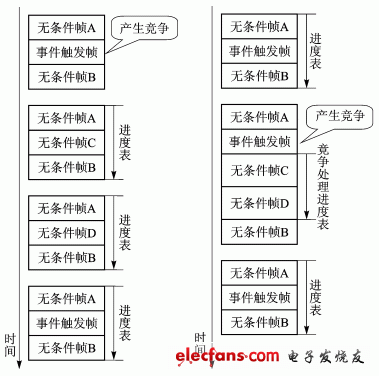
Figure 1 LIN2.0 event-triggered frame contention processing mechanism Figure 2 LIN2.1 event-triggered frame contention processing mechanism
1.2 Improvement of node configuration function
1.2.1 Added the function of assigning a series of frame IDs
Change the configuration function to assign a frame ID to assign a series of frame IDs. The format of the frame ID allocation in the LIN2.0 and LIN2.1 protocols is shown in Figure 3. In LIN2.0, the allocation can only succeed if both NAD and Supplier ID match, but only one frame ID can be allocated at a time. In LIN2.1, only NAD matching is required. Up to 4 frame IDs can be assigned each time, and the Message ID in LIN2.0 has been cancelled in LIN2.1. The purpose of this improvement is to increase the efficiency of the LIN network configuration. After the change, the speed of assigning the frame ID can be up to 4 times the original.
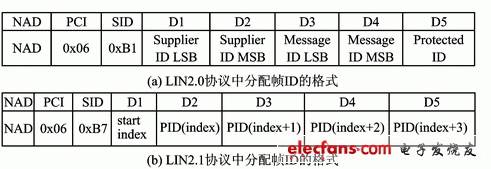
Figure 3 The format of the frame ID allocation in the LIN2.0 and LIN2.1 protocols
1.2.2 Add the function of saving configuration
The LIN2.1 protocol has added the function of saving the configuration information of the slave node, and the configuration information of the slave node is stored in the non-volatile storage space after power failure. In this way, the configuration of the master node to the slave node will not be lost after reset.
1.3 Diagnostic grade
Another big new feature of LIN2.1 is that the node will be divided into 3 levels according to the diagnosis function.
(1) Diagnosis level
Diagnosis level 1 is generally used for devices such as smart sensors or actuators that do not require or require very few diagnostic functions. The diagnostic level supports all node configuration functions and only requires single frame transmission.
(2) Level 2 diagnosis
Compared with the first level of diagnosis, the node of the second level of diagnosis adds the function of node identification. For example, users can obtain the software and hardware version numbers of products. In addition, Diagnostic Level 2 also supports reading and writing of internal software parameters, such as temperature and speed. Diagnostic level 2 supports multi-frame transmission.
(3) Three levels of diagnosis
Diagnosis of the three-level node not only contains all the functions of the previous two levels, but also supports the internal flash erase and write, users can program through the LIN bus. Diagnostic level 3 supports multi-frame transmission.
Coin/Button Cell-retainers And Contacts
Antenk coin cell battery retainers Designed for memory back-up and stand-by applications, these contacts permit quick and easy coin cell replacement and installation. Eliminating "soldered-in" cells, computer, video, telecommunication and similar PCB based product users now have a reliable, "no tools required" method for changing batteries.
Extremely economical, these retainer contacts are available in surface mount (SMT) or thru hole mount (THM) styles for 4.8mm, 6.8mm, 11.6mm,12mm, 16mm, 20mm, 23mm and 24mm coin cells. The THM version has stable mounting legs for excellent board retention during wave solder. The SMT version includes a unique solder tail "flow-hole" design to bolster reflow and strengthen solder joints. They are manufactured from phosphor bronze, precision stamped and are plated with either a high luster nickel finish or matte tin finish ideal for low temperature soldering enviornments. Both feature dual spring contacts to assure reliable connections and a low contact resistance.
Antenk Coin/Button Cell-retainers And Contacts

Coin cell retainers are simple metal contacts that both electrically connect coin cells and hold them in place, while taking up minimal additional space on the PCB. They feature nickel-plating, and since most coin cells have nickel shells this helps to prevent galvanic corrosion, an electrochemical process that can damage dissimilar metals that are in electrical contact. Our retainers are always designed with automation in mind, and can be easily picked and placed, with both through hole and surface mount retainers available for most coin cell sizes. Combining the ease of automation with the low cost of Antenk's retainers, it is no wonder they are such a popular product.
Coin Cell, Button Cell, Retainers, Contacts
Designed for memory backup and standby applications, Antenk's compact coin cell battery retainers permit quick and easy coin cell replacement and installation. By eliminating soldered-in cells, computer, video, telecommunication, and similar PCB based product users now have a reliable, no tools required method for changing batteries.
These holders and retainers are available in surface-mount (SMT) or through-hole-mount (THM) styles for 4.8 mm to 24 mm coin cells. The THM version has stable mounting legs for excellent board retention during wave soldering. The SMT version includes a unique solder tail flow-holedesign to bolster reflow and strengthen solder joints. Both feature dual spring contacts to assure reliable connections and low contact resistance.
Coin Cell, Button Cell, Retainers, Contacts Features
Available in THM or SMT configurations
SMT solder tail with flow-hole design for increased joint strength
SMT solder tail located outside of retainer body which facilitates visual inspection of the solder joints
THM legs maintain relative position during and after soldering
Reliable spring tension assures low contact resistance
Retains battery securely to withstand shock and vibration
Ideally suited for high-density packaging
Ideal for low-profile space-saving PCB applications
Designed for reflow and all PCB soldering applications
Compatible with all wave and reflow operations
Compatible with most vacuum and mechanical, pick and place assembly systems
Matte-tin plate for lower soldering temperatures ideal where other temperature sensitive components are being used
Tin-nickel plated retainers are ideal for lead-free, high-temperature soldering applications
Retainers available for coin cell batteries from 4.8 mm to 24 mm diameter
Coin Cell Retainers by Size of Cell
191 | 335 | CR1025 | CR1216 | CR1220 | CR1225 | CR1632 | CR2016 | CR2032 | CR2320 | CR2325 | CR2330 | CR2354 | CR2430 | CR2450 | CR2477 | F3 iButton | F5 iButton | LR1120 | LR44 | ML414 | SR512SW | SR60 | V80H or CP1654 | BR1025 | BR1216 | BR1220 | BR1225 | BR1632 | BR2016 | BR2032 | BR2320 | BR2325 | BR2330 | BR2450 | BR2477 | Other Sizes
Button Contacts,Coin Cell Retainers And Contacts,Coin Cell Retainers
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.pcbsocket.com