On December 7, 2015, the US Aviation Weekly article introduced the centennial growth of modern aero-engines and several significant and landmark milestones.

Rotary cylinder star engine
An engine designed by an early engine manufacturer is a structure in which the crankshaft is fixed to the aircraft fuselage, and the entire crankcase and cylinder are rotated to provide sufficient cooling air for the engine, so that it is not necessary to equip the engine with a radiator, thereby reducing the weight of the engine. The concept was first pioneered by French automotive engineers Louis and Laurent Seguin, who founded the Société des Moteurs Gnome in Gennevilliers near Paris in 1905, followed by "Rona Motors" in 1912. (Société des Moteurs Le Rhôn) merged into the "Gnomish and Rhone" rotary engine company, whose engines were commonly used by Allied and German aircraft during the First World War.
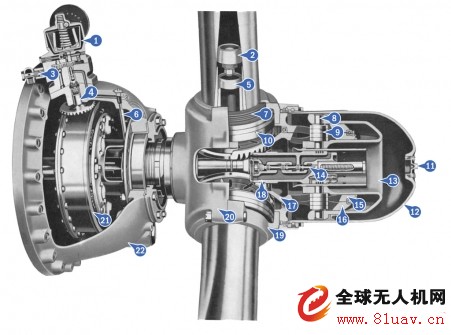
Variable pitch propeller
In order to have better climb performance and higher engine efficiency during flight, the propeller pitch is changed. Hamilton Standard developed the first practical system to change blade angles in flight; it was installed on Douglas DC-1 aircraft for commercial service in 1933. Further development of the electro-hydraulic servo variable pitch system, and finally developed a constant speed adjustable pitch propeller, with the speed increase the governor will automatically increase the pitch. The main components of the system are: 1) governor; 2) paddle pins; 3) auxiliary oil connector; 4) governor drive; 5) spider arm; 6) governor oil circuit; Oil seal from paddle to barrel; 8) camshaft; 9) cam roller; 10) thrust bearing assembly; 11) fairing plug; 12) fairing housing; 13) piston; 14) distributor valve; ) cam bearing; 16) stationary cam; 17) rotating cam; 18) blade gear section; 19) front half barrel shell; 20) rear half barrel shell; 21) propeller reduction gear; 22) engine head section.

Turbocharger
At the end of World War I, the researchers found that before the sea level air was drawn into the engine, it was usually pre-compressed by a centrifugal compressor to significantly increase the power of the piston engine. The system is also used to compensate for the reduced air density as height increases, thereby preventing power degradation during aircraft climbs. The early "Liberty" engine was equipped with a basic turbocharger, and in 1918 a team led by General Electric (GE) Sanford Moss tested a similar turbocharger.

Liquid cooled power unit
In order to pursue lower drag and higher flight speeds, some piston engine cylinders are arranged in a row rather than radially. However, in the face of the challenge of cooling air, the designer chose to use a liquid cooling system. In the 1940s, the development of a powerful liquid-cooled piston engine reached its peak. The British company's "Merlin" (Merlin) engine produced thousands of units during World War II as fighters and bombers. And the power of the transport plane.

Ultimate piston engine
The power of the piston finally reached its peak, such as Pratt & Whitney's 2,800-horsepower R-2800 "Double Wasp" and the 3,500-horsepower R-4360 "Wasp Major" engine. The 18-cylinder 2,200-horsepower R-3350 duplex swirl developed by Curtis Wright and the 3,700-horsepower turbo compound with three GE turbochargers. As the last and most advanced mass-produced piston passenger aircraft at the time, Douglas' DC-7C and Lockheed's Super Constellation, Wright's turbo compound engine is Wright's first four-cylinder engine. 280 times.
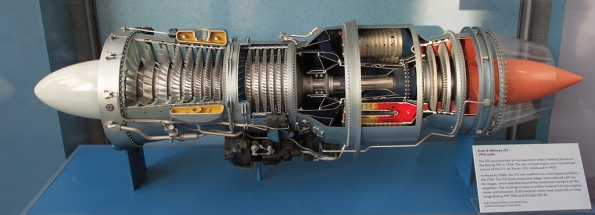
Double rotor turbojet
After the Second World War, Pratt & Whitney developed the first dual-rotor (or two-shaft) turbojet with two compressors and turbines installed concentrically in the same engine. The resulting J57 became the gold standard of that era and became the driving force for various US military aircraft, from Boeing's B-52 and KC-135 to McDonnell's F-101, Convair. The F-102 and various naval aircraft, including Douglas' F4D and F5D. The J57 also made the North American YF-100 aircraft the first fighter to achieve sustained supersonic flight in 1953. Pratt & Whitney also provided the J57 civilian-derived JT3 engine to the civilian market, becoming the power of the first generation Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 series aircraft. A British engine, Bristol (later Rolls-Royce) Olympus engine is also a dual-rotor construction, after the initial operation in 1950, as a "Vulcan" bomber Powered and partnered with Snecma to power the Anglo-French Concorde supersonic transport.

Shenzhen Chaoran Technology Corp. , https://www.chaoran-remote.com